BPMN engine
BPMN engine tries to adhere to the bpmn 2 specification and be compatible with Camunda 8. The engine can be used through the ZenBPM platform or as a standalone library.
The engine is fully instrumented via OpenTelemetry:
- Tracing: Each process, token, and flow node has spans.
- Metrics: Tracks counts of started, ended processes, worker executions etc.
Storage
The engine uses a storage interface to interact with storage systems. ZenBPM platform implements a solution based on RqLite database. The codebase also provides a default implementation for in memory storage that is used by the engine's Unit tests.
Node processing in the engine
Internally the engine uses "Tokens" as a pointers that traverse the diagram and represent execution state. Tokens are manipulated based on node logic (e.g., split for gateways, wait for messages/timers). One loop through the engine's main loop means processing the token's flow node and outgoing sequence flows.
Execution Tokens
Tokens (ExecutionToken) track progress through flow nodes:
Key: Unique identifier.ElementId: ID of the current BPMN element.State: Running, Waiting, Completed, Failed.
Exclusive Gateway example
The following example shows processing of an Exclusive Gateway.
Since Exclusive Gateway cannot create parallel flows the token gets reused and continues to flow through the diagram.
Parallel Gateway example
The following example shows processing of a Parallel Gateway.
To keep track of the parallel executions the token that activated the gateway is completed and outgoing parallel flows get assigned a new tokens that each represents a parallel execution flow.
Interacting with the BPMN engine
Business Key
For the correlation of process instances to external business entities businessKey attribute can optionally be used. This attribute allows you to efficiently identify the process instance which is associated with the business entity.
For usage please see OpenAPI.
Workers
Supported elements
TODO: we should split these into separate pages with examples.
Start event
Start event is fully supported.
End event
End event is fully supported.
Service task
Fully supported through external workers.
User task
Fully supported through external workers.
Business rule task
Supported through internal dmn engine.
Call activity
The subprocess for call activity is started on the same partition as the process that invoked it.
Parallel gateway
Current implementation handles parallel flows correctly if there is only one overlapping flow in the process instance. Multiple recursive parallel flows have currently undefined behaviour.
Inclusive gateway
Inclusive gateway is fully supported.
Exclusive gateway
Exclusive gateway is fully supported.
Event based gateway
Event based gateway currently supports message and timer events.
Message catch event
A Message Catch Event is used to model the recipient of a message from an external participant or process. It indicates that the execution flow will pause until the specified message is received. ZenBPM implementation of the engine tries to provide guarantees that only one message is active in the system with the same name and correlation key.
Uniqueness Message Catch Event is identified by a Correlation Key and Correlation Name. Combination of the two parameters is unique for each message catch event. Running into Message Catch Event with an already existing combination results in Incident(link).
Message subscription
Message subscription is what we refer to when the engine stores data about the Message Catch Event.
Message subscription pointer
Message subscription pointers are used to correlate messages in Zen's architecture of a distributed system. Pointers are used to efficiently determine location of a stored subscription, without requiring any internal identifiers. Pointer's storage partition is calculated from user defined Correlation Key. From which we can determine partition assigned to Message Subscription and its Process Instance to then correlate the message.
Usage
Messages can be published through API or by triggering Intermediate throw event.
Publish a message
Request Body schema: application/jsonrequired
| correlationKey required | string |
| messageName required | string |
| variables | object |
Responses
Request samples
- Payload
{- "correlationKey": "011-235-813",
- "messageName": "payment-received",
- "variables": {
- "paymentId": "pay-123-abc",
- "amount": 1000,
- "currency": "USD",
- "receivedAt": "2025-08-22T16:25:10Z"
}
}Response samples
- 400
- 502
{- "code": "NOT_FOUND",
- "message": "Process instance with key 4503599627370501 not found"
}We plan to implement message start event along with timer start events in the future
Link intermediate throw event
Link intermediate throw event is fully supported.
Link intermediate catch event
Link intermediate catch event is fully supported.
Timer intermediate catch event
Timer intermediate catch event is fully supported.
Boundary event
Boundary events of supported event types are supported. The boundary event subscriptions are created at the time of token reaching waiting state.
Both interrupting and non-interrupting boundary events are supported.
Currently supported activity types with boundary events:
- ServiceTask,
- SendTask,
- UserTask,
- BusinessRuleTask,
- CallActivity
Currently supported event types with boundary events:
- Message,
- Timer
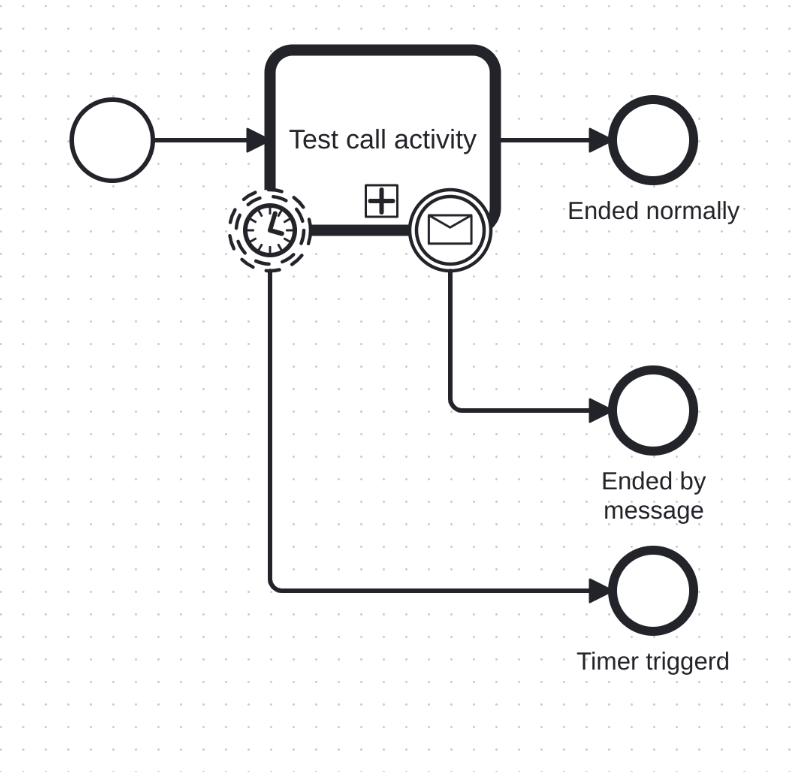 Boundary event usage example
Boundary event usage example
XML parser
TODO: add information about how we are parsing xml definitions of processes